As of late, analysts led by Prof. Huang Qing from the Institute of Intelligent Machines, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), proposed another strategy to consider the cell reinforcement action of astaxanthin isomers in contrast to singlet oxygen.
The outcomes were published in Food Chemistry.
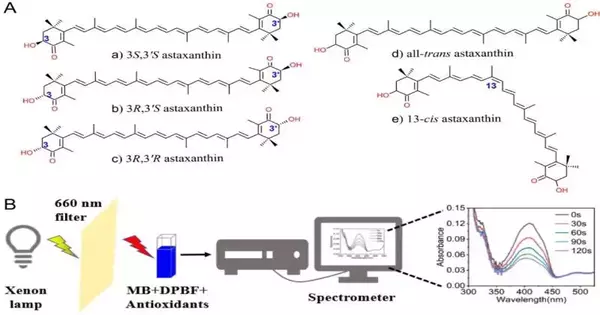
Astaxanthin has great cell reinforcement properties and is widely utilized in food supplements. It has numerous isomers and their physical and compound properties are likewise unique. The group has been dealing with the wellspring of astaxanthin properties and capabilities for quite a long time. In this review, they attempted a spectroscopic strategy to explore the cell reinforcement action of isomers of astaxanthin against singlet oxygen (1O2). Singlet oxygen is a sort of receptive oxygen species (ROS) with a long life and a solid oxidation limit. Previously, concentrating on the cell reinforcement action of astaxanthin didn’t explicitly recognize the dynamic oxygen species and by and large overlooked the distinction in cancer prevention agent action of astaxanthin’s isomers.
In past examinations, researchers utilized methylene blue (MB) as a photosensitizer to create 1O2, and they utilized test 1, 3-diphenyliso-benzofuran (DPBF) to identify 1O2 in the arrangement. The singlet oxygen extinguishing limits of astaxanthin isomers were assessed by looking at the retention changes of DPBF at 410 nm under various astaxanthin treatments, and the extinguishing constants of astaxanthin isomers were contrasted with those of vitamin E.
The investigation discovered that the singlet oxygen extinguishing steady of astaxanthin was three significant degrees different from that of vitamin E. The 1O2 extinguishing limits of the optical isomers of astaxanthin are practically indistinguishable in extracellular tests. For the cis-trans mathematical isomers of astaxanthin, the 1O2 extinguishing limit of cis-astaxanthin was altogether higher than that of all-trans astaxanthin.
It offered a straightforward and easy spectroscopic strategy to survey the cell reinforcement action of various types of astaxanthin against singlet oxygen and uncovered huge contrasts between mathematical isomers, which gave another premise to the viable use of astaxanthin in the food business and the improvement of future organic capabilities.
More information: Xinxin Zheng et al, Assessment of the antioxidant activities of representative optical and geometric isomers of astaxanthin against singlet oxygen in solution by a spectroscopic approach, Food Chemistry (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133584
Journal information: Food Chemistry