A Chinese group has distributed new work in Energy Material Advances.
“In 2017, we detailed another group of 2D progress metal borides as analogs to MXenes and begat a snappy name for them, MBenes,” said paper creator Zhimei Sun, teacher of the School of Materials Science and Designing at Beihang College.
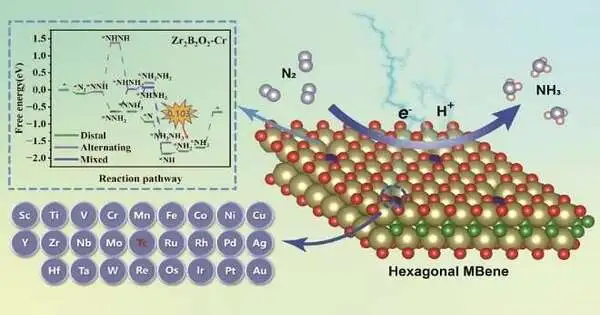
“Up till now, MBenes have been broadly concentrated as impetuses or substrates of different responses, including HER, ORR/OER, NRR, and CO2RR. MBenes with orthorhombic structures are the focus of most research into their electrocatalytic performance, while h-MBenes (or hexagonal MBenes) are the subject of few studies.”
Sun explained that the excellent electrical conductivity, mechanical properties, and electronic properties of MBenes make them excellent catalysts. In particular, some researchers predicted that some MBenes would have phases that were hexagonal rather than their orthorhombic counterparts.
“MBenes have been extensively studied as catalysts or substrates in a variety of reactions, including HER, ORR/OER, NRR, and CO2RR.” Notably, research into the electrocatalytic performance of MBenes has been focused on those with orthorhombic structures, with few investigations on using hexagonal MBenes (h-MBenes) as electrocatalysts.”
Zhimei Sun, professor of the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Beihang University.
“The dynamic and thermal stabilities of Zr(Hf)2B2 have been verified in earlier investigations, and it has been predicted that hexagonal Zr2B2 and Hf2B2 have the chance of being exfoliated.”
In addition, they exhibit high metallic conductivity, ensuring efficient electron transfer. What’s more, in the interim, Zr2B2 displays high hypothetical limits and low movement energy hindrances for Li+ and Na+, exhibiting the extraordinary possibilities of those anticipated materials for electrochemical energy stockpiling and transformation.”
Notwithstanding, concerning electrocatalysts, the absence of dynamic locales and compelling charge communities is a significant issue, making it challenging to initiate reactants. Single-atom catalysts (SACs), which typically have increased reactivity and high selectivity toward particular products, present a unique opportunity for the creation of electrocatalysts.
In particular, it has been demonstrated that MBenes have brilliant physical and synthetic attributes, which are profoundly wanted as substrates for single-particle impetuses.
Sun and her team systematically investigated the electrocatalytic NRR performance of a series of transition metal atoms (e.g., 3d, 4d, and 5d) embedded in defective hexagonal MBene nanosheets (h-Zr(Hf)2B2O2) in order to investigate the potential applications of hexagonal Zr2B2 and Hf2B2 as NRR electrocatalysts. They discovered that h-Zr(Hf)2B2
“Zr2B2O2-Cr stood out with high selectivity to NRR against HER and an ultra-low limiting potential (0.10 V),” Sun stated. “Based on our proposed screening criteria, 16 candidates were efficiently selected out of 50 systems. “The value is much lower than the well-known stepped Ru (0001) surface (0.43 V).”
“The beginning of the great action is credited to the synergistic impact of the single iota (SA) and the M particles in the substrate. In addition, a composition descriptor based on the catalysts’ inherent characteristics (number of valence electrons of SAs, electronegativity of SAs, and Zr(Hf) atoms) was proposed, which aids in better predicting the catalytic performance.
In addition to identifying effective NRR electrocatalysts, this work also paves a new path for the application of h-MBenes, which will spur additional experimental and theoretical efforts to develop this novel 2D material.
More information: Ya Gao et al, Hexagonal MBenes-Supported Single Atom as Electrocatalysts for the Nitrogen Reduction Reaction, Energy Material Advances (2023). DOI: 10.34133/energymatadv.0039