Various studies have shown that time-limited eating and remembering increases for life length in research center studies, making practices like intermittent fasting a hotly debated issue in the health industry.Be that as it may, precisely what it means for the body on the atomic level and how those changes interface across numerous organ frameworks has not been known with certainty.
Presently, Salk researchers show in mice what time-confined eating means for quality articulation across in excess of 22 districts of the body and mind. Quality articulation is the interaction through which qualities are enacted and answer their current circumstances by making proteins.
The discoveries, distributed in Cell Digestion on January 3, 2023, have suggestions for an extensive variety of medical issues where time-confined eating has shown expected benefits, including diabetes, coronary illness, hypertension, and disease.
“We discovered that time-restricted eating had a system-wide, molecular impact in mice. Our findings pave the way for further investigation into how this nutritional intervention activates genes linked in specific disorders such as cancer.”
Professor Satchidananda Panda,
“We observed that there is a framework-wide, sub-atomic effect of time-limited eating in mice,” says Teacher Satchidananda Panda, senior creator and holder of the Rita and Richard Atkinson Seat at Salk. “Our outcomes open the door for looking all the more carefully at how this dietary mediation enacts qualities engaged with explicit infections, like malignant growth.”
For the review, two gatherings of mice underwent a similar unhealthy eating routine. One gathering was given free admittance to the food. The other gathering was confined to eating inside a nine-hour window every day. Following seven weeks, tissue samples from 22 organs and the mind were collected at various times of the day and night and examined for hereditary changes.Tests included tissues from the liver, stomach, lungs, heart, adrenal organ, nerve center, various pieces of the kidney and digestive tract, and various regions of the cerebrum.
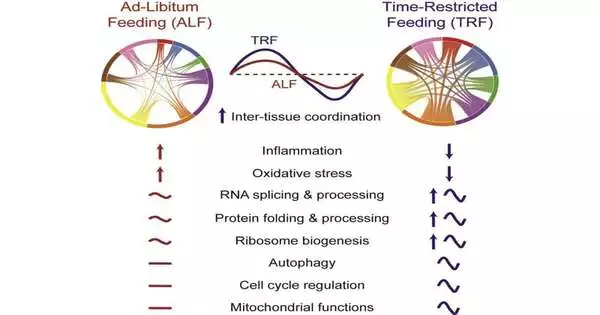
According to the creators, 70% of mouse characteristics respond to time-limited eating.
“By changing the planning of food, we had the option to change the quality articulation not simply in the stomach or in the liver, but additionally in a large number of qualities in the mind,” says Panda.
Almost 40% of qualities in the adrenal organ, nerve center, and pancreas were impacted by time-confined eating. These organs are significant for hormonal regulation. Chemicals coordinate capabilities in various pieces of the body and mind, and hormonal irregularity is embroiled in numerous illnesses, from diabetes to stretch problems. The outcomes offer direction for how time-confined eating might assist with dealing with these infections.
Curiously, not all segments of the intestinal system were impacted similarly. While qualities engaged with the upper two bits of the small digestive system Wthe duodenum and jejunumwiwere actuated by time-limited eating, the ileum, at the lower end of the small digestive tract, was not.
This finding could open another line of exploration to concentrate on how occupations with shiftwork, which disturb our 24-hour organic clock (called the circadian mood), influence stomach-related infections and malignant growths. Past examination by Panda’s group showed that time-confined eating worked on the strength of firefighters, who are commonly shift workers.
The scientists likewise figured out that confined eating adjusted the circadian rhythms of different organs of the body.
“Circadian rhythms are present in every cell,” Panda says.”We figured out that the opportunity confined eating synchronized the circadian rhythms to have two significant waves: one during fasting and another soon after eating.” We suspect this permits the body to arrange various cycles.
Panda’s group will then investigate the effects of time-limited eating on specific circumstances or frameworks involved in the study, for example, atherosclerosis, which is a hardening of the supply routes that is frequently a precursor to coronary illness and stroke, as well as chronic kidney disease.
More information: Shaunak Deota et al, Diurnal transcriptome landscape of a multi-tissue response to time-restricted feeding in mammals, Cell Metabolism (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.12.006
Journal information: Cell Metabolism