In a new exhaustive survey distributed in Boondocks of Ecological Science and Designing on December 5, 2023, specialists from Tsinghua College dig into different creative techniques for the expulsion of radioactive cesium from wastewater.
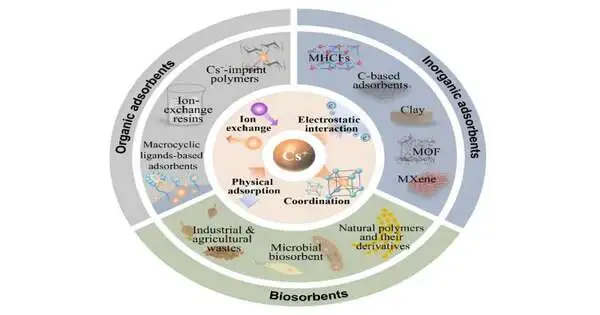
Analysts evaluate a few adsorption and film detachment strategies utilized in cesium expulsion in this survey. They investigate a scope of adsorbents, sorting them into inorganic, natural, and organic materials, and assess their viability in catching cesium particles. They additionally examine layer-based division techniques, including reverse assimilation, forward assimilation, and film refining, featuring their parts in cesium particle detachment.
Exceptional consideration is given to the techniques utilized in the cleanup endeavors following the Fukushima Daiichi atomic mishap, particularly the Kurion/SARRY framework, the desalination framework, and the High-Level Fluid Handling Framework (ALPS). Given cesium’s extraordinary properties, for example, its little hydrated span and high dissemination coefficient, these techniques face critical difficulties in successfully disconnecting cesium particles from water.
“Removing radioactive cesium from wastewater is more than a scientific challenge; it is also necessary for maintaining ecological balance and public health. Adsorption and membrane separation methods have advanced significantly, but further innovation is required.”
Professor Jianlong Wang, the corresponding author of this review,
Teacher Jianlong Wang, the relating creator of this survey, remarks, “The undertaking of eliminating radioactive cesium from wastewater isn’t simply a logical test, but rather a need for keeping up with environmental equilibrium and general wellbeing. The headways in adsorption and film division advances address huge forward moving steps, yet ceaseless development is fundamental.”
The survey infers that the expulsion of radioactive cesium is a complex yet fundamental endeavor. Adsorption arises as a profoundly viable technique for overseeing low convergences of radionuclides in enormous volumes of wastewater, with specific materials showing excellent adsorption limits and selectivity. Film division advances; for example, switch assimilation likewise assumes a pivotal role, particularly in the Fukushima cleanup.
In spite of the advancement, the audit highlights the requirement for additional headways, especially in tending to difficulties like the therapy of concentrated maintenance fluid and upgrading the radiation security of film materials. The discoveries highlight the significance of these advancements in shielding the climate and general wellbeing from the risks of atomic exercise.
More information: Shuting Zhuang et al, Cesium removal from radioactive wastewater by adsorption and membrane technology, Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s11783-024-1798-1