Detecting frameworks are becoming increasingly common in many aspects of our lives, including medical care, autonomous vehicles, and touchless human-PC interaction.Be that as it may, these frameworks frequently need knowledge: they will quite often accumulate all suitable data, regardless of whether it is important. This can lead not exclusively to protection encroachments, but also to sitting around, energy consumption, and computational assets during information handling.
To resolve this issue, specialists from the French CNRS thought of an idea for smart electromagnetic detection that utilizes AI procedures to create learned brightening designs in order to pre-select important subtleties during the estimation cycle. A programmable metasurface is designed to produce the learned examples, performing high-exactness detection (e.g., act acknowledgment) with a strikingly diminished number of estimations.
However, estimation processes in reasonable applications are unavoidably dependent upon an assortment of disturbances. In a general sense, commotion goes with any estimation. The signal-to-commotion proportion can be especially low in indoor conditions, where the emanated electromagnetic signals should be kept weak.
“We faithfully hope that our results can be transferred to information-extraction issues based on other wave phenomena (e.g., optics, acoustics, elastics, and quantum mechanics) and/or with other forms of in-situ programmable measurement gear,”
Chenqi Qian and Philipp del Hougne furthered previous research .
Consequently, Chenqi Qian and Philipp del Hougne facilitated past exploration and introduced a canny programmable computational meta-imager that not just fits its light example to a particular data extraction task like item acknowledgment but additionally adjusts to various kinds and levels of commotion. They distributed a welcome research article on their outcomes in Keen Registering on December 2, 2022.
“We conjecture that the ideal lucid brightening examples to be utilized by a savvy programmable meta-imager to proficiently remove task-explicit data from a scene will significantly depend upon the kind and level of clamor,” the scientists expressed, bringing up that commotion may significantly influence the ideal meta-imager designs in light of the fact that, other than dormancy imperatives, which restrict the quantity of permitted estimations, commotion likewise restricts how much data can be extricated from the scene.
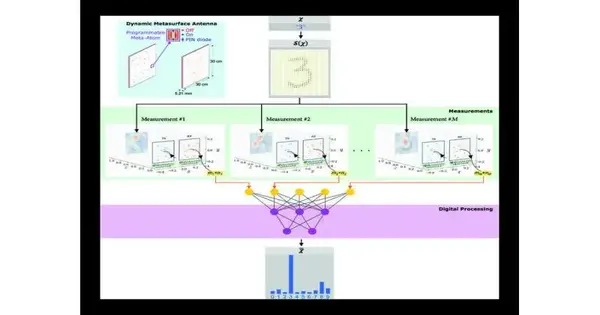
“In this paper, we methodically investigate how the blend of dormancy imperatives and clamor influences savvy multi-shot programmable meta-imagers,” the specialists said. To assess their speculation, the specialists thought about a prototypical item acknowledgment issue, for which they proposed a microwave computational programmable meta-imager framework. Such frameworks could be conveyed in indoor reconnaissance, earth perception, and so forth.
In their considered framework, one microwave dynamic metasurface radio wire (DMA) emanated a succession of lucid wavefronts to the scene using a solitary transmitter, and a second DMA soundly caught the reflected waves using a solitary identifier. A differentiable start-to-finish data stream pipeline was formed, which involved the programmable actual estimation process, including commotion, along with the resulting computerized handling layers.
The fundamental components of this pipeline are no different for all wave-based data extraction issues, including imaging, detecting, limitation, and item acknowledgment. “The primary significant distinction lies in the explicit expense capability that will be streamlined for good execution,” they concluded.
The same approach used by the creators to protest acknowledgment can thus be used in boundary assessment issues such as confinement.”This pipeline permits us to mutually converse and plan the programmable actual loads (DMA setups that decide the intelligent scene enlightenments) and the teachable computerized loads.”
This joint enhancement—task-explicit start to finish joint streamlining of the teachable actual boundaries and teachable computerized boundaries—endows the estimation cycle with task mindfulness to the point where it can distinguish between task-significant and task-immaterial data over the air in the simple space.
The experts tested the demonstration of this programmable meta-imager that generates a series of error explicit and commotion explicit scene enlightenments and discovered it invaluable over conventional compacted detecting with irregular designs when the data that can be removed from the scene is restricted by inactivity limitations as well as clamor.The exhibition gains for a sign with no substance disturbance and a sign with added substance disturbance were both shown.The “naturally visible” elements of the learned brightening designs, in particular their shared covers and forces, were viewed as naturally reasonable notwithstanding the “discovery” nature of the methodology.
As indicated by the scientists, the progress toward a framework that self-adaptively identifies the sort and level of commotion and updates as needed in its use of DMA setups without extra human information is clear. “We are confident that our results can be applied to data extraction issues in light of other wave peculiarities (e.g., optics, acoustics, elastics, and quantum mechanics) as well as various types of in-situ programmable estimation equipment,” they concluded.
More information: Chenqi Qian et al, Noise-Adaptive Intelligent Programmable Meta-Imager, Intelligent Computing (2022). DOI: 10.34133/2022/9825738