Care rehearses are reflective activities that urge individuals to carry their attention to what they are encountering right now while making an effort not to decipher or pass judgment on these encounters. Investigations have discovered that these practices can have various advantages, for example, easing pressure, working on the nature of rest, and supporting the handling of feelings.
Practices pointed toward cultivating care (i.e., a psychological state set apart by receptiveness, mindfulness, and consideration of the current second) are presently utilized as psychotherapeutic devices in numerous nations around the world. They are likewise a pivotal part of numerous psychotherapy draws, for example, care-based mental treatment (MBCT), acknowledgment and responsibility treatment (ACT), and the care-based pressure decrease (MBSR) program made by Prof. Jon Kabat-Zinn.
Specialists at the College of Wisconsin-Madison and Virginia Federation College have as of late done a review pointed toward researching the impacts of brief care rehearsals on the association of huge-scope cerebrum organizations and on cozy accomplice hostility.
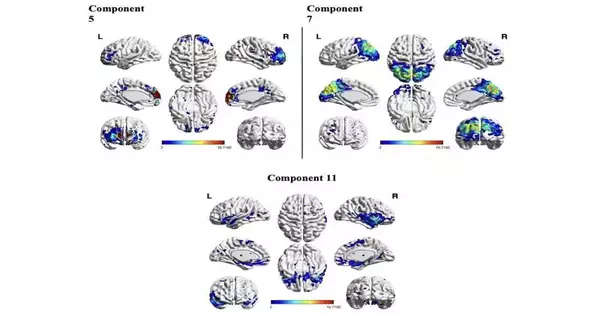
“Mindfulness instruction decreased coherence in the default mode network while increasing functional connectivity in the frontoparietal control and salience networks,”
Rahrig, Ma and their colleagues wrote.
Their discoveries, distributed in mental, emotional, and social neuroscience, recommend that even a couple of moments of consideration-based care reflection prompt observable changes in the action and association of pivotal brain organizations.
“Care can deliver neuroplastic changes that help versatile mental and profound working,” Hadley Rahrig, Liangsuo Mama, and their associates wrote in their paper.
“As of late, interest in single-practice care guidance has developed impressively as a result of the coming of portable wellbeing innovation. In like manner, the ongoing review looked to broaden brain models of care by exploring transient conditions of care during single-portion openness to centered consideration reflection.”
The information broken down by Rahrig, Mama, and their teammates was gathered as a feature of a bigger report exploring close connections. This study included 51 grown-up heterosexual couples who had been dating for something like a half year.
These couples were isolated and requested to finish either a 10-minute care reflection practice or a 10-minute unwinding exercise. The cerebrum movement of these members was recorded utilizing attractive reverberation imaging (X-ray), a harmless procedure that catches pictures of the mind or different designs in the human body utilizing attractive and radio waves.
The couples were consequently likewise requested to finish a responsibility assessment assessing their conduct and hostility, where they needed to press a button quicker than their rivals. These rivals, which were, as a matter of fact, mechanized by a PC program, were supposed to be either more odd, a dear companion, or their personal accomplice.
The group’s examination of trial information yielded fascinating outcomes, which lined up with different discoveries accumulated previously. In particular, the analysts found that the 10-minute care contemplation practice expanded utilitarian availability inside the frontoparietal control organization (FPCN) and the remarkable quality organization (SN), while decreasing cognizance in the purported default mode organization (DMN).
While it affected cerebrum network designs, the short-care preparation didn’t fundamentally influence the animosity that members showed towards what they accepted to be their significant others during the conduct task. This doesn’t guarantee that care rehearsals don’t assist with decreasing forceful ways of behaving; it just proposes that such a short preparation doesn’t.
“Care guidance diminished intelligence inside the default mode organization and expanded utilitarian availability inside the frontoparietal control and notability organizations,” Rahrig, Mama, and their partners composed.
“Moreover, care decouples essential visual and consideration-connected networks. However, this acceptance couldn’t evoke changes in ensuing close accomplice animosity, and such hostility was extensively unrelated to any of our organization’s records. These discoveries propose that negligible portions of centered, consideration-based care can advance transient changes in huge-scope cerebrum networks that have unsure ramifications for forceful ways of behaving.”
In general, the discoveries assembled by these specialists show that even a short-term contemplation exercise can impact the association and movement of enormous-scope brain circuits.
In light of the noticed changes in the members’ cerebrums after the activities, Rahrig, Mama, and their partners guess that care advances the decoupling between mind areas related to the handling of visual upgrades and brain networks connected with consideration.
This new review could before long prepare for an additional examination investigating the effect of both periodic and customary care rehearsals on brain availability, private accomplice animosity, and maybe different ways of behaving in heartfelt connections. By and large, this work could assist with divulging other expected advantages of care practices and their consequences for the cerebrum.
More information: Hadley Rahrig et al, Inside the mindful moment: The effects of brief mindfulness practice on large-scale network organization and intimate partner aggression, Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience (2023). DOI: 10.3758/s13415-023-01136-x.