Drop microfluidics provides a solid platform for orchestrating and functionalizing miniature and nanoparticles in a variety of applications, including drug conveyance, screening, lab-on-a-chip, and organ-on-a-chip applications in synthetic and biomedical design.Chitosan is a biomaterial appropriate for different biomedical applications, incorporating antibacterial bioactivities with resistant improving and anticancer properties. In another report currently distributed in Scientific Reports, Omid Sartipzadeh and an interdisciplinary exploration group in clinical nanotechnology, biomaterials, and tissue design in Tehran, Iran, depicted the job of chitosan drops in a microfluidic chip. The results demonstrated how various sizes and calculations of the chitosan drops could be laid out by differing the boundaries for a few purposes, including drug conveyance, tissue designing, and cell embodiment. The group directed a trial concentrate on that concurred with the recreation results to affirm the outcomes.
Tissue design and microfluidics
Monodisperse miniature and nanoparticles stand out across lab-on-a-chip instruments and biosensors for a scope of utilization in tissue designing. Materials scientists and bioengineers have made numerous efforts to create uniform miniature and nano-particles on demand.In any case, the interfacial strains between stages have made it challenging to furnish appropriate miniature and nanoparticles with top caliber. Since run of the mill methods are exorbitant, complex, and tedious, specialists attempt to produce monodisperse miniatures and nanoparticles with on-request morphology, shapes, and sizes.
In this work, Sartipzadeh et al. researched the microfluidics bead age rates, including stream speed, by means of COMSOL Multiphysics test system programming to create functional microfluidic chips for chitosan-oil-chitosan twofold emulsions. They originally explored different avenues regarding a model of computational liquid elements to comprehend the design and highlights of beads to make a stream-centered microchannel. Using the recreations, they found a way to deal with and accomplish a more profound understanding of the complex on-chip process. The results permitted the group to join two immiscible liquids and their speed to analyze bead development, drop breadth, and their pace of age.
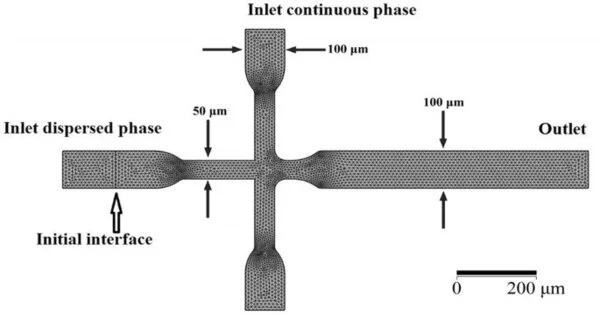
The example of the MFFD applied in recreations: lattices and limits circumstances determined for the microfluidic drop generatrix in the two-aspect model. Image courtesy of Scientific Reports (2022).DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12031-9
The methodology
Sartipzadeh et al. fostered the trial techniques considering the results of the reenactment. They examined the physical and substance properties of chitosan and doxorubicin, a kind of anthracycline/chemotherapy drug, in comparison with drop size and pace of drop creation. The group decided the example and speed of the parts, utilizing a microfluidics stream centering gadget (MFFD) to decide bead size and creation rates. In view of the results, the group accomplished a complete technique to make microfluidic beads. The MFFDs kept up with bays and outlet channels to control scattered and immiscible liquid streams crashing into one another at a crossing point. The researchers noticed how the drops were directed downstream of the principal conduit in view of the tension angle and speed of the arrangement to shape four degrees of stream. The going with depictions from the reenactments represented the bead setup as a subordinate of time with shifting convergences of chitosan and doxorubicin. Sartipzadeh et al. planned and fostered the example of microfluidic stream shaping on a silicon wafer utilizing delicate lithography and cast the form of the microfluidic stream centering gadget with polydimethylsiloxane. The group reinforced the form of chip designs onto a slide glass through oxygen plasma, then, at that point, infused the constituents into the chip by utilizing two siphons to look at the systems of consolidated microgel drop creation.
Elements of drop development
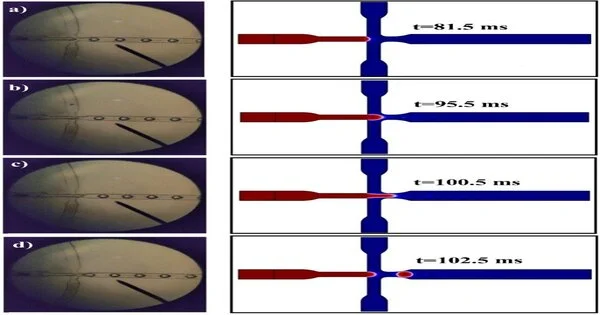
The CS (chitosan) with a grouping of 0.2% and 13.75 mg of DOX (doxorubicin) per ml of CS arrangement. The checking electron magnifying instrument (SEM) of the result CS + DOX microgel drop of the trial result showed that the volumetric stream pace of the CS + DOX stage was 3.3 mm/s and the volumetric stream pace of the oil stage was 11.1 mm/s. Image courtesy of Scientific Reports (2022).DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12031-9
The group investigated the elements of tension-coordinated fluid bead development, where they noticed a huge expansion in the strain, contrasting with the tension when the cycle. The peculiarity depends on the power of strain, shear pressure, and surface pressure. At the point when the strain and shear pressure were more prominent than the surface elastic power, the bead started to thicken and thin. Moreover, the power balance between the boundaries of strain, shear pressure, and surface strain depends on the actual properties of the arrangements of interest. The group investigated the centralization of the constituents, compared with the components of the bead, and demonstrated a harmony between shearing force and interfacial pressure. They determined the fluid stream and its impact on a few applications, remembering lab-for chip immunoassays, and they determined the size of beads comparative with constituent fixations, including the recurrence of drop age and the quantity of drops framed in the review. The group attributed the results to a few boundaries on the stage.
The doxorubicin chemotherapy drug’s drug discharge profiles
Sartipzadeh et al. then, at that point, fostered a chitosan-doxorubicin blend with various groupings of chitosan blended in with a particular measure of the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin, to grasp the reliance of drop width on thickness. The rising centralization of chitosan prompted an increment in its dynamic thickness to create drops of fluctuating breadths. The group next researched the arrival of doxorubicin from chitosan in the lab, to show how the medication discharge profile followed a two-way design, and to feature the job of chitosan as microcarriers of semi-designated conveyance frameworks. The researchers analyzed the medication discharge profiles from the microcarriers at two unique temperatures and pH levels, to feature the harmfulness of epitomized doxorubicin on malignant growth cells contrasted with the free medication. The presence of the transporter made the course of medication discharge more biocompatible for sound cells when contrasted with the harmfulness of the medication in its free structure.
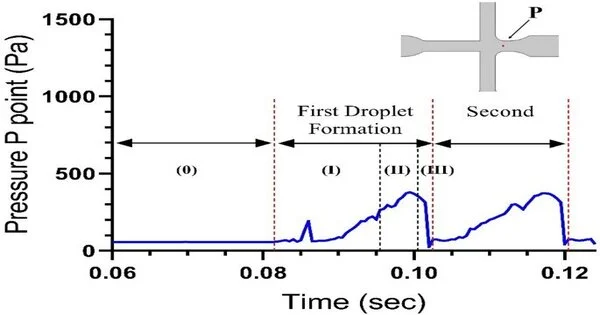
The system of the tension slant at the P point, however long the bead arrangement might last, The P point concludes the point arranged at the fundamental conduit section. It reflects the improvement of the drop arrangement process. Three stages of bead arrangement are: (I) lag, (II) filling, and (III) necking. The CS+DOX speed is steady at 3.3 mm/s, and the speed of vegetable oil is equivalent to 11.1 mm/s. Image courtesy of Scientific Reports (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12031-9
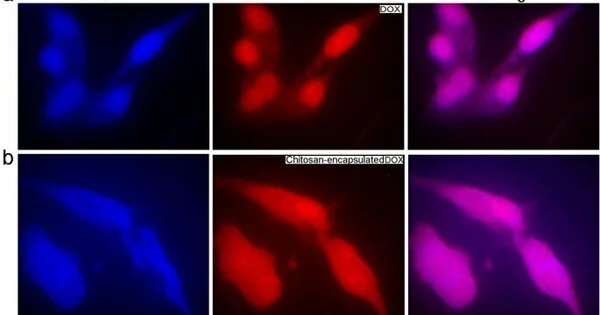
(a) Cellular uptake of DOX by the MCF-7 bosom malignant growth cell line (b) Cellular uptake of CS-DOX by the MCF-7 bosom malignant growth cell line. DAPI is utilized to stain the cores of cells. Because of its fluorescent nature, DOX makes the cell cytoplasm become red on the fluorescent imaging. The pictures affirm the take-up of the medication by the cells. Image courtesy of Scientific Reports (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12031-9
Viewpoint
Along these lines, Omid Sartipzadeh and partners fostered a computational liquid elements model to comprehend the course of biocompatible chitosan drop aspects and development in a stream-centered microchannel. The reenactment results featured a substitute way to deal with arriving at the normal trial results. In view of the examinations, the group underscored the meaning of chitosan microparticles for drug conveyance applications in biomedicine. The great bioactivity, biocompatibility, and biodegradability made the material appropriate for different applications in a microfluidic gadget, including drug screening on lab-on-a-chip stages and medication conveyance inside organ-on-a-chip instruments, with 3D cell societies to evaluate the poisonousness of medication competitors. The group directed a proof-of-idea examination to address critical difficulties in biomedicine and featured the use of chitosan beads as microcarriers for designated drug treatment.