Doctors frequently recommend gadolinium implantation to improve X-ray filters, but there is evidence that nanoparticles of the harmful rare earth metal penetrate kidney cells, in some cases causing serious side effects, according to College of New Mexico specialists.
In the most pessimistic scenarios, gadolinium, a component that has no biologic capability, can set off nephrogenic fundamental fibrosis, a difficult illness that influences the skin and organs and is frequently deadly.
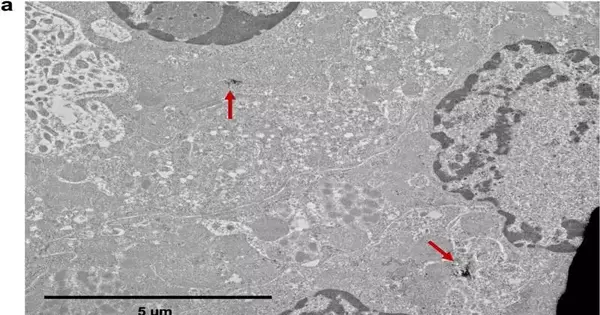
In another review distributed in Logical Reports, a group led by Brent Wagner, MD, MS, academic administrator in the UNM Division of Inner Medication, portrays the utilization of electron microscopy to identify minuscule stores of gadolinium in the kidneys of individuals who had been infused with contrast agents before their X-rays.
“Patients have developed the full-blown illness after only one injection. Some people were ill eight years after being exposed. There have even been accounts of persons having symptoms after receiving heart or kidney transplants.”
Brent Wagner, MD, MS, associate professor in the UNM Department of Internal Medicine,
“These are nanoparticles,” Wagner said. “They’re really shaping nanomaterials inside these cells.”
Gadolinium-based contrast specialists were first introduced during the 1990s, as X-ray studies turned out to be more common practice, he said. Gadolinium lines up with an X-ray scanner’s strong attractive field, making for more honed pictures, but because of its poisonousness, the metal should firmly attract undoubtedly chelating particles, so it very well may be sifted through the kidneys and wiped out.
In any case, the analysts have found that some gadolinium particles can filter out of the different specialists and into the kidneys and other tissues, Wagner said. The impact was found in both rat and human examples, he said.
“We got five tissues from patients with X-ray contrast openness accounts and another five from control patients who were contrast-gullible, and I was shocked because each of the five presented to the difference specialist had gadolinium in it.”
According to Wagner, gadolinium-containing contrast agents are used in roughly half of all X-ray exams.A significant inquiry is why certain individuals foster the infection, yet the vast majority of those who are uncovered never display negative side effects.
“Patients have gotten the out-and-out illness after a solitary portion,” he said. “Some have gotten infections eight years after being open.” There are even reports of individuals who got heart or kidney transplants and experienced side effects.
The chances of creating sickness seem to increase with more noteworthy openness to the differentiation specialist and as gadolinium stores develop in tissues, Wagner said. “There are individuals who get five portions, and afterward you can begin recognizing the gadolinium inside the cerebrum when you do an X-ray with no difference.”
It’s hazy how a portion of the gadolinium isolates from the chelating particles, he said.
“The central issue is how this differentiation specialist frees the gadolinium and adjusts its affidavit in the cell,” said Wagner, who also serves as the director of the Kidney Organization of New Mexico and the renal segment manager for the New Mexico Veterans Undertakings Medical Services Framework.
The review brought together associates from the UNM Division of Earth and Planetary Sciences, the UNM Branch of Math and Measurements, the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, the New Mexico VA Wellbeing Framework, and the Middle for Incorporated Nanotechnologies at Los Alamos Public Research Center and Sandia Public Labs.
Wagner voiced worries about the inescapable utilization of gadolinium-based contrast specialists, recommending that numerous doctors probably won’t know about the dangers. “Frequently, contrast is given where it’s not requiredn or perhaps you don’t for a moment even need an X-ray.”
Another source of concern is that gadolinium is, by all accounts, finding its way into the environment.Since the X-ray contrast specialist is excreted through pee, it gets into sewer frameworks, but wastewater treatment plants aren’t prepared to eliminate it, he said.
Gadolinium levels have grown twentyfold in the San Francisco Straight, and in Germany, gadolinium can be recognized in soda pops produced using regular water. A similar peculiarity is obvious in New Mexico, he said.
“We as a whole went out to different wellsprings of surface water, snatched samples, and had them estimated at UNM,” Wagner said. “The Rio Grande at Alameda had gigantic levels.”
Gadolinium seems to set off the arrival of white platelets called fibrocytes. “At the point when they get into the skin, they begin partaking in injury repair,” he said. However, in instances of fundamental fibrosis, “it resembles atypical injury mending.”
Yet, Wagner figures there may be a method for breaking this cycle to help diabetes patients on dialysis. “They’ll almost always have extremely unfortunate injury mending,” he says. “I like to see possible upsides as well as figuring out what the component of sickness is.”
More information: Joshua DeAguero et al, The onset of rare earth metallosis begins with renal gadolinium-rich nanoparticles from magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent exposure, Scientific Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-28666-1