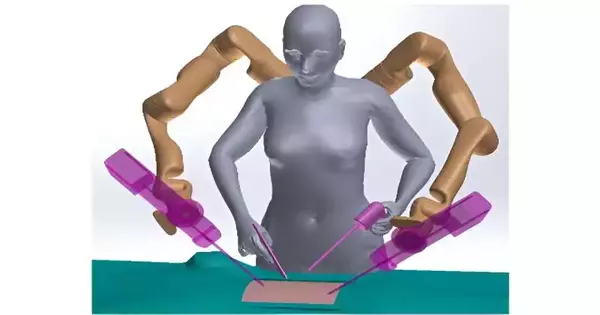
Another study by scientists at Sovereign Mary College of London, Royal School London, and The College of Melbourne found that individuals can figure out how to involve exaggerated mechanical arms as well as working with an accomplice in only one hour of preparation.
The review, distributed in the IEEE Open Diary of Designing in Medication and Science, researched the capability of effusive automated arms to assist individuals with performing assignments that require multiple hands. The possibility of human expansion with extra counterfeit appendages has for quite some time been highlighted in sci-fi, as in Specialist Octopus in The Astonishing Bug Man (1963).
“Many daily chores, like opening a door while carrying a large item, require more than two hands. Supernumerary robotic arms have been offered as a solution to help humans perform these jobs more readily, but up until now, it was unclear how simple they would be to operate.”
said Dr. Ekaterina Ivanova, lead author of the study from Queen Mary University of London.
“Many errands in day-to-day existence, for example, opening an entryway while conveying a major bundle, require multiple hands,” said Dr. Ekaterina Ivanova, lead creator of the review from Sovereign Mary College of London. “Exaggerated mechanical arms have been proposed as a method for permitting individuals to do these errands all the more effectively, yet as of not long ago, it was not satisfactory the way that simple they are used.”
The review included 24 members who were approached to play out various undertakings with an exaggerated mechanical arm. The members were either given one hour of preparation on how to utilize the arm or they were approached to work with an accomplice. Credit: Sovereign Mary, College of London
The outcomes showed that the members who had gotten prepared on the exaggerated arm played out the undertakings similarly as well as the members who were working with an accomplice. This proposes that exaggerated mechanical arms can be a practical option in contrast to working with an accomplice and that they can be figured out how to utilize successfully in a somewhat short amount of time.
“Our discoveries are promising for the advancement of exaggerated automated arms,” said Dr. Ivanova. “They recommend that these arms could be utilized to assist individuals with various undertakings, like a medical procedure, modern work, or recovery.”
More information: Yanpei Huang et al, Can Training Make Three Arms Better Than Two Heads for Trimanual Coordination?, IEEE Open Journal of Engineering in Medicine and Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1109/OJEMB.2023.3305808