The development of exceptionally proficient fake photosynthesis frameworks to change over CO2 into flexible synthetic substances is a supportable pathway to reduce an Earth-wide temperature boost and the continuous energy emergency. To bring fake photosynthetic advances towards down-to-earth applications, a carbon pattern of CO2 decrease combined with H2O oxidation is viewed as an optimal way to convert sun-based energy into synthetic energy, as performed by photosynthesis in nature.
In any case, the critical motor hindrance for the water oxidation response restricts the photocatalytic proficiency of the CO2 decrease. Hence, extra electron conciliatory specialists have been utilized as electron givers to advance the photocatalytic decrease of CO2.
Nonetheless, the utilization of conciliatory specialists isn’t just monetarily impossible, yet it additionally squanders the oxidation limit of the photogenerated openings. In such a manner, coupling the CO2 decrease process with the oxidation of organics to yield value-added synthetics is a promising methodology for commonsense application. Besides, assuming the organics are gotten from biomass, basically inexhaustible feedstocks are consumed.
To further develop the electron move proficiency in the photocatalytic framework, specialists have endeavored to abbreviate the distance between the impetus and the photosensitizer by building a’span’ between them. In any case, convoluted engineered techniques are expected notwithstanding valuable metal-based impetuses, and the conceivable breakage of covalent bonds during the electron transport cycle might bring about an irreversible misfortune in the steadiness and action of the framework.
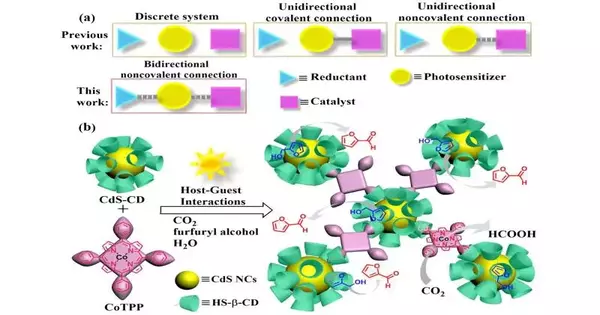
As of late, an examination group led by Prof. Tong-Bu Lu from Tianjin College of Innovation, China, announced the bidirectional host-visitor cooperation between the photosensitizer and the impetus/reactant, in which the impetus and the reactant were simultaneously assembled on the outer layer of the photosensitizer.
The immediate contact between the photosensitizer and the impetus or reactant abbreviates the transmission distance of photogenerated transporters, which subsequently can decisively support the photocatalytic CO2 decrease to HCOOH, with a yield of 1610 μmol g-1 h-1 and a selectivity of 96.5%. In the mean time, the photogenerated openings in Cds can likewise be immediately demolished by β-Compact disc fortified furfuryl liquor, achieving a furfural yield of 1567 μmol g-1 h-1 and > close to 100% selectivity.
This work opens another course to the simple development of profoundly productive counterfeit photosynthesis frameworks for pragmatic application. The outcomes were distributed in the Chinese Diary of Catalysis.
More information: Wen Zhang et al, Bidirectional host-guest interactions promote selective photocatalytic CO2 reduction coupled with alcohol oxidation in aqueous solution, Chinese Journal of Catalysis (2023). DOI: 10.1016/S1872-2067(23)64509-7