With an end goal to make the web more open for individuals with inabilities, specialists at The Ohio State College have started fostering a man-made brainpower specialist that could finish complex jobs on any site utilizing straightforward language orders.
In the thirty years since it was first delivered to the public, the internet has turned into an extraordinarily unpredictable and unique framework. However, in light of the fact that web capability is presently so fundamental to society’s prosperity, its intricacy additionally makes it significantly harder to explore.
Today, there are billions of sites accessible to assist with getting to data or speaking with others, and many undertakings on the web can find in excess of twelve ways to finish. That is the reason Yu Su, co-creator of the review and an associate teacher of software engineering and design at Ohio State, said their work, which utilizes data taken from live locales to make web specialists—online simulated intelligence partners—is a stage toward making the advanced world a less befuddling place.
“Some people, particularly those with disabilities, find it difficult to use the internet. We rely more and more on the technological world in our daily lives and at work, yet there are growing many hurdles to that access, which contributes to the discrepancy.”
Yu Su, co-author of the study and an assistant professor of computer science and engineering at Ohio State,
“For certain individuals, particularly those with incapacities, it’s difficult for them to peruse the web,” said Su. “We depend increasingly more on the registering scene in our day-to-day existence and work; however, there are progressively a ton of boundaries to that entrance, which somewhat enlarges the dissimilarity.”
The review was introduced in December at the Thirty-seventh Meeting on Brain Data Handling Frameworks (NeurIPS), a lead gathering for man-made intelligence and AI research. It is accessible on the arXiv preprint server.
By exploiting the force of huge language models, the specialist works in much the same way as people act while perusing the web, said Su. The Ohio State group showed that their model had the option to comprehend the design and usefulness of various sites, utilizing just its capacity to process and anticipate language.
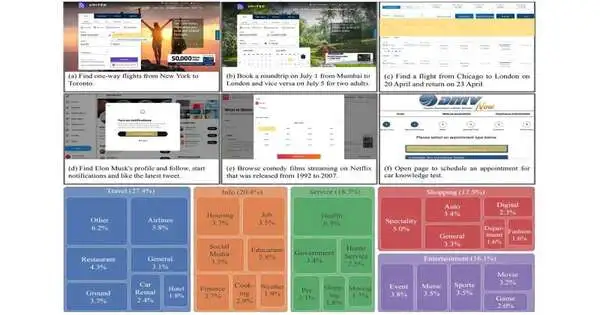
Specialists began the interaction by making Mind2Web, the first dataset for generalist web specialists. However, past endeavors to construct web specialists zeroed in on toy mimicked sites, Mind2Web completely embraces the perplexing and dynamic nature of true sites and underlines a specialist’s capacity to sum up altogether new sites it has never seen.
Su said that quite a bit of their prosperity is because of their representatives’ capacity to deal with the web’s consistently developing expectation to learn and adapt. The group lifted north of 2,000 unassuming assignments from 137 distinct genuine sites, which they then, at that point, used to prepare the specialist.
A portion of the undertakings included booking one-way and full-circle global flights, following big-name accounts on Twitter, perusing parody films from 1992 to 2017 gushing on Netflix, and, in any event, planning vehicle information tests at the DMV. A significant number of the undertakings were extremely mind-boggling—for instance, booking one of the global flights utilized in the model would make 14 moves. Such easy flexibility considers different inclusions on various sites and opens up another scene for future models to investigate and learn in an independent style, said Su.
“It’s simply become conceivable to follow through with something like this due to the new advancement of huge language models like ChatGPT,” said Su. Since the chatbot became public in November 2022, a great many clients have utilized it to consequently produce content, from verse and jokes to cooking counsel and clinical conclusions.
In any case, since one site could contain a huge number of crude HTML components, it would be excessively exorbitant to take care of such a lot of data for a single enormous language model. To address this hole, the concentrate likewise presents a structure called MindAct, a two-dimensional specialist that utilizes both little and huge language models to do these errands. The group found that by utilizing this system, MindAct fundamentally beats other normal displaying methodologies and can grasp different ideas at a respectable level.
With all the adjustments the review brings up, the model could almost certainly be utilized in pairs with both open- and closed-source enormous language models like Flan-T5 or GPT-4. Notwithstanding, their work features an undeniably important moral issue in making adaptable computerized reasoning, said Su. While it could unquestionably act as an accommodating specialist for people riding the web, the model could likewise be utilized to upgrade frameworks like ChatGPT and transform the whole web into a remarkably integral asset, said Su.
“From one perspective, we can possibly work on our productivity and permit us to zero in on the most imaginative piece of our work,” he said. “In any case, then again, there’s gigantic potential for hurt.” For example, independent specialists ready to make an interpretation of online strides into this present reality might impact society by making actually risky moves, for example, abusing monetary data or spreading deception.
“We ought to be very careful about these elements and put forth a coordinated attempt to attempt to moderate them,” said Su. In any case, as computer-based intelligence research keeps on advancing, he takes note that it’s logical that society will encounter significant developments in the business use and execution of generalist web specialists in the years to come, particularly as the innovation has previously acquired such ubiquity in the public eye.
“All through my profession, my objective has forever been to attempt to overcome any issues between human clients and the processing scene,” said Su. “All things considered, the genuine worth of this instrument is that it will truly save individuals time and make the unthinkable conceivable.”
More information: Xiang Deng et al, Mind2Web: Towards a Generalist Agent for the Web, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2306.06070