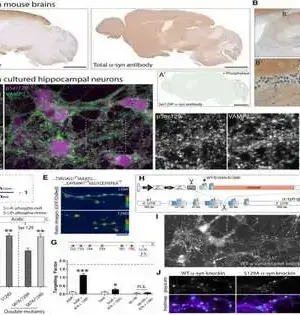
Oxytocin is a chemical created in the minds of people and different creatures, specifically in a locale known as the nerve center. Otherwise called the chemical of affection, it has a vital impact on friendly holding, generation, and labor. Lately, a few neuroscientists have been examining the likely advantages of oxytocin organization for lessening tension and psychosocial stress as well as supporting mental cycles. While a portion of these examinations accomplished intriguing outcomes, the useful and possibly helpful impacts of oxytocin organization are yet to be plainly depicted. Scientists at So Paulo University recently conducted a study to see if
Neuroscience
Perhaps the best test in the area of nervous system science and serious consideration of medication is accurately diagnosing the degree of cognizance of a patient in a trance state because of extreme mind injury. Researchers of the Human Mind Task (HBP) have presently investigated new methods that might be able to more readily distinguish two unique neurological circumstances. Their discoveries, published in the journal eLife, uncover significant data on the systems of awareness. The group of scientists from the College of Liège, GIGA Cognizance Exploration Unit and Unconsciousness Science Gathering and CHU de Liège (Belgium), Universitat Pompeu Fabra (Spain),
Dietary decisions and their results may surely impact mental capability. Another review driven by examiners at Brigham and Ladies' Clinic, an establishing individual from the Mass General Brigham medical care framework, alongside outside partners, develops recently distributed work (zeroed in on Puerto Rican people in the U.S.) by including extra races and identities. The group tracked down that specific plasma metabolites—substances made when the body separates food—were related to worldwide mental capability scores across the assorted arrangements of races and identities. Their outcomes are categorized as Alzheimer's and Dementia. "Our review has immense qualities in growing the example size and
A new University of California, Irvine-led study reveals how mechanical forces and tissue mechanics influence the morphology of the developing brain, and establishes a direct link in neural stem cells between Piezo1, a mechanically-activated ion channel, and intracellular cholesterol levels during neural development. The study, titled, "Piezo1 regulates cholesterol biosynthesis to influence neural stem cell fate during brain development," was published today in the Journal of General Physiology. Study findings demonstrate a role for Piezo1 in the neurodevelopmental process that modulates the quantity, quality, and organization of cells by influencing cellular cholesterol metabolism. "Our surprising discovery linking Piezo1 and cholesterol also motivates investigations
About 10 years after the role of pyramidal neurons in mental portrayals of room and area was found, a gathering of Brazilian and American specialists has made a significant commitment to how researchers might interpret the mind's route framework by recognizing a subtype of these neurons that can check speed with extraordinary accuracy. In tests including creatures, we showed a relationship between the electrical action of inhibitory interneurons and speed portrayals in the mind," Alexandre Kihara, a neuroscientist at the Government College of the ABC in So Paulo state, Brazil, told Agência FAPESP. Kihara is a co-writer of an article
Scientists at Universitätsmedizin Berlin and the Maximum Planck Organization for Natural Knowledge (right now during the time spent being laid out) have uncovered the exact associations between tactile neurons inside the retina and the predominant colliculus, a structure in the midbrain. The Neuropixels tests are a moderately late turn of events, addressing the up and coming age of terminals. Neuropixels tests, which are densely packed with recording focuses, are used to record the actions of nerve cells, and they have worked with these new bits of knowledge into neuronal circuits.Writing in Nature Correspondences, the scientists depict an essential rule that
Neuroscientists have been attempting to comprehend how creatures and people process tactile data for quite a few years at this point. While their work has prompted numerous significant disclosures, many inquiries stay unanswered. In warm-blooded creatures and numerous different creatures, smells are presently known to be handled by the olfactory bulb, a cerebrum district toward the front of the mind. The olfactory bulb then sends data connected with olfaction and smells to different regions in the body, so it may very well be handled further. Scientists at the College of Pennsylvania Institute of Medication have as of late done a
Researchers at the Foundation of Neuroimmunology and Various Sclerosis Exploration at the College Clinical Center Göttingen have found that pathogenic safe cells utilize the inward, delicate layers of the meninges yet not the external hard layer to attack the sensory system and trigger damaging irritation. The meninges are altogether engaged in the illness cycle of various sclerosis (MS). In this ongoing fiery illness of the focal sensory system, unique safe cells erroneously assault the patient's own mental tissue. The meninges do more than just act as a door for the foolish cells to enter the mind; they are likewise where
Cedars-Sinai examiners have fostered an investigational treatment utilizing support cells and a defensive protein that can be conveyed past the blood-cerebrum obstruction. This consolidated undeveloped cell and quality treatment might possibly safeguard sick engine neurons in the spinal cord of patients with amyotrophic long-term sclerosis, a deadly neurological issue known as ALS, or Lou Gehrig's illness. The Cedars-Sinai group demonstrated in the primary preliminary of its kind that the conveyance of this consolidated treatment is safe in people.The discoveries are accounted for now in the companion explored diary, Nature Medicine. "Utilizing undeveloped cells is a strong method for conveying significant
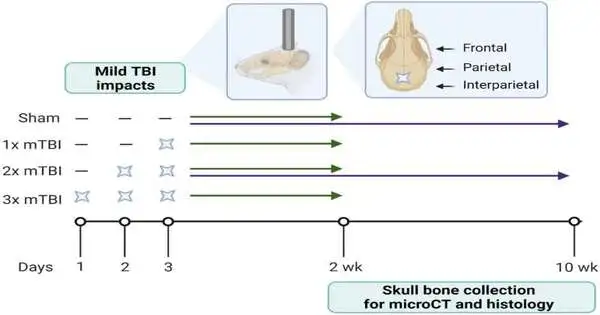
New exploration has found that rehashed blackouts can thicken the design of skull bones. Past examinations have shown harm to the mind following blackout, yet they have not checked the cerebrum's defensive covering out. A Monash-drove concentrate on, distributed in the journal Scientific Reports by Associate Professor Bridgette Semple from Monash University's Central Clinical School Department of Neuroscience, found that rehashed blackouts brought about thicker, denser bones in the skull. It is hazy whether this thickening of the skull is something to be thankful for or something terrible. In principle, a thicker skull is a more grounded skull, proposing that