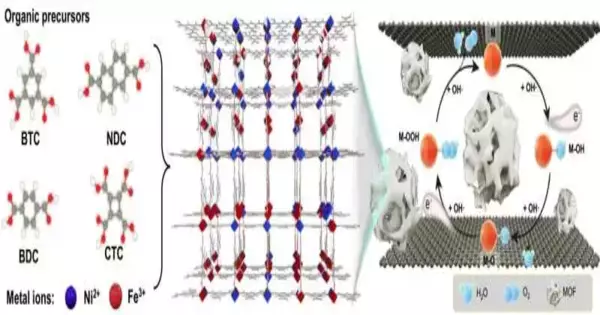
At Prof. Zhang Tao’s gathering at the Ningbo Foundation of Materials Innovation and Designing (NIMTE) of the Chinese Institute of Sciences (CAS), he, as a team with Prof. Hou Yang from Zhejiang College and Prof. Xiao Jianping from the Dalian Foundation of Compound Material Science of CAS, proposed a clever two-layered (2D) nanoconfinement system to firmly upgrade the oxygen development response (OER) action of low-conductivity metal-natural structures (MOFs). Results were distributed in Nature Correspondences.
The advancement of high-proficiency electrocatalysts for the electrochemical change of water to create harmless to the ecosystem and feasible hydrogen energy has drawn huge consideration for quite a long time.
Despite the critical role that OER plays in water parting, OER at the anode necessitates a relatively high thermodynamic potential to accelerate water parting energy.Because of the huge surface region, tunable porosity, various pieces and metal focuses, MOFs have arisen as promising contenders for effective OER electrocatalysts. In any case, the naturally unfortunate conductivity of most MOFs truly blocks their reactant action.
To resolve this issue, scientists at NIMTE proposed an electrochemical technique to keep MOFs between graphene multi-facets through the two-cathode electrochemical framework, thus blessing inadequately conductive MOFs with firmly upgraded reactant execution.
The as-arranged NiFe-MOF/G shows a strikingly low overpotential of 106 mV to arrive at 10 Mama cm-2, outperforming the perfect NiFe-MOF as well as other recently detailed MOFs and their subordinates. Plus, the NiFe-MOF/G anode is profoundly steady, which can hold the exhibition for in excess of 150 h at 10 Mama cm-2 without clear action rot.
However, the consequences of X-beam retention spectroscopy tests and thickness useful hypothesis estimations show that the nanoconfinement from graphene multi-facets advances the electronic design and catalysis focus of MOF materials with the development of profoundly receptive NiO6-FeO5 twisted octahedral species in MOF structure. Also, the nanoconfinement brings down the potential for water oxidation response.
The nanoconfinement system can be applied to other shifted MOFs with various designs, incredibly working on their electro catalytic exercises. Meanwhile, this work challenges the conventional origination of perfect MOFs as idle impetuses and demonstrates the extraordinary application capability of insufficiently conductive or, in any case, protecting MOFs in electro catalysis applications.
More information: Siliu Lyu et al, Exceptional catalytic activity of oxygen evolution reaction via two-dimensional graphene multilayer confined metal-organic frameworks, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33847-z
Journal information: Nature Communications