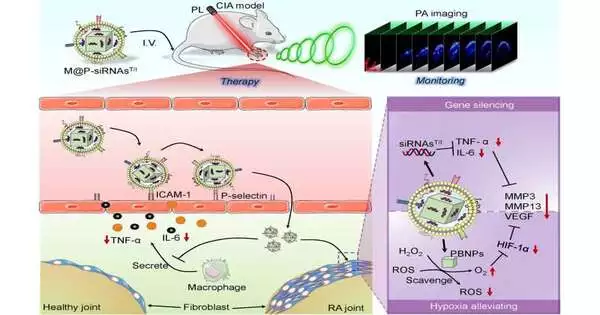
The elevated degree of responsive oxygen species (ROS) in the rheumatoid joint inflammation (RA) microenvironment and its diligent fiery nature can cause harm to joints, bones, and the synovium. Methodologies that coordinate viable RA microenvironment guidelines with imaging-based checking could prompt enhancements in the analysis and treatment of RA.
A joint exploration group from the Shenzhen Establishment of Cutting-edge Innovation of the Chinese Foundation of Sciences and the College of Texas at Austin has proposed another methodology that can accomplish designated treatment of rheumatoid joint pain.
The specialists coordinated little meddling RNAs (siRNAsT/I) and Prussian blue nanoparticles (PBNPs) to quiet the declaration of the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-/IL-6 and search for the ROS related to the RA microenvironment.
The review was published in PNAS on October 18.
To upgrade the in vitro and in vivo natural steadiness, biocompatibility, and focusing on the ability of the siRNAsT/I and PBNPs, the specialists arranged macrophage film vesicles (MMVs) to build biomimetic nanoparticles, M@P-siRNAsT/I.
They tracked down that the M@P-siRNAsT/I stifled TNF-/IL-6 articulation and defeated the hypoxic idea of the RA microenvironment, hence reducing RA-prompted joint harm in a mouse model.
Also, close infrared photoacoustic imaging (PAI) permitted the focusing on conduct of the M@P-siRNAsT/I to be continued progressively, thus allowing an assessment of their helpful viability without the requirement for obtrusive methods.
These discoveries show that macrophage-biomimetic M@P-siRNAsT/I and their analogs helped by PAI can give another procedure for RA determination, treatment, and observing.
The exploration was published in the Procedures of the Public Foundation of Sciences.
More information: Jianhai Chen et al, Photoacoustic image-guided biomimetic nanoparticles targeting rheumatoid arthritis, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2022). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2213373119
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences