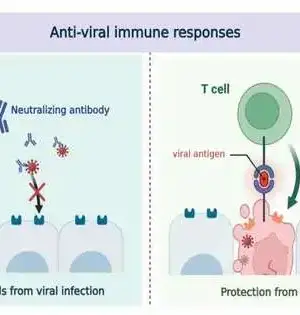
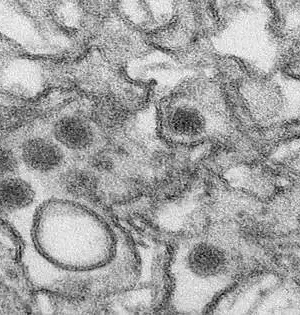
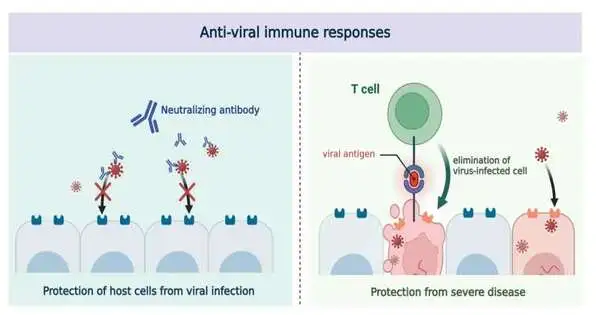
It has been a long time, starting from the beginning of the coronavirus pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 still can't seem to be annihilated, and new variations are persistently arising. In spite of the broad vaccination programs, advancement diseases (contamination after immunization) by new variations are normal. A new examination recommends that human-resistant reactions are additionally changing to battle the endless rise of new SARS-CoV-2 variations. In particular, it has been found that the safe framework that experienced advancement contamination by the omicron variation gets upgraded resistance against future variants of the omicron. The review is distributed in Science Immunology. A group of
Immunology
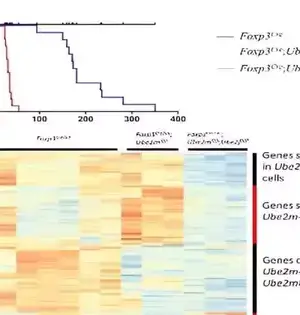
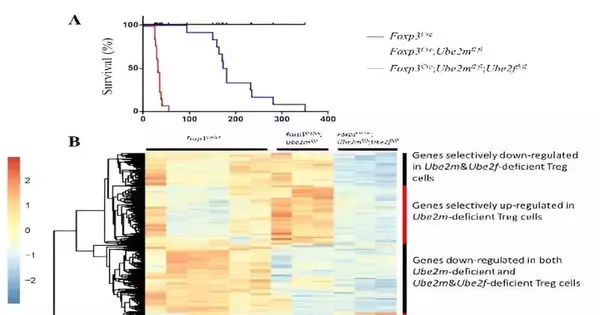
Teacher Yi Sun's group at Zhejiang College reports a utilitarian compensatory impact between the Ube2m-Rbx1 and Ube2f-Droop tomahawks of the neddylation-Cullin-RING ligases (CRLs) framework in Treg cells, utilizing restrictive KO mouse models. The group likewise uncovered that both Ube2m-Rbx1 and Ube2f-Droop tomahawks are basically expected for the elements of Treg cells and explained robotically that the Rbx1/Hang CRLs have capability in both neddylation-subordinate and autonomous habits. Considering that strange initiation of CRLs (e.g., by upgraded cullin neddylation) is related to numerous human immune system illnesses, for example, foundational lupus erythematosus, incendiary entrail sickness, and rheumatoid joint inflammation, this work might
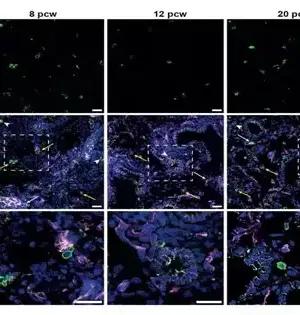
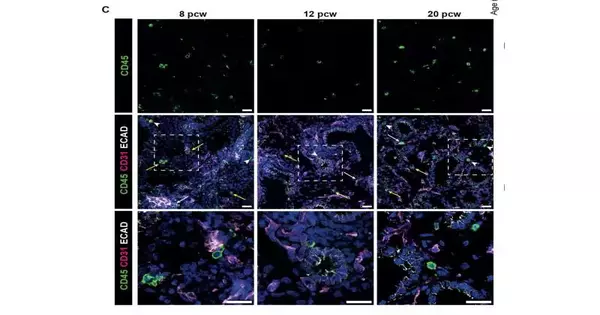
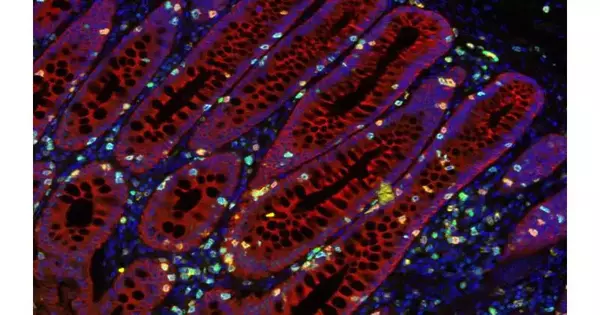
Safe cells assume a functioning and cozy role in coordinating the development of human lung tissue during improvement, scientists find, upsetting our comprehension of how we might interpret early lung advancement and the job of resistant cells beyond invulnerability. The examination offers new experiences for understanding and treating respiratory circumstances, like ongoing obstructive aspiratory infection (COPD). Nearly 20% of all deaths involving children under the age of five worldwide are caused by respiratory conditions. The work uncovers amazing coordination between the safe and respiratory frameworks, significantly sooner being developed than recently suspected. This disclosure brings up issues about the likely
A significant clinical preliminary study, driven by specialists at the College of Nottingham, has shown that individuals with fiery circumstances can further develop the immunizer reaction from a coronavirus promoter immunization by intruding on their treatment for quite some time following having the immunization. The neutralizer reaction to the hit was multiplied at four weeks and one and a half times more prominent at 26 weeks, when contrasted with the individuals who went on with their treatment to the surprise of no one. The superior neutralizer reaction went on for a considerable length of time. Patients who hindered treatment detailed
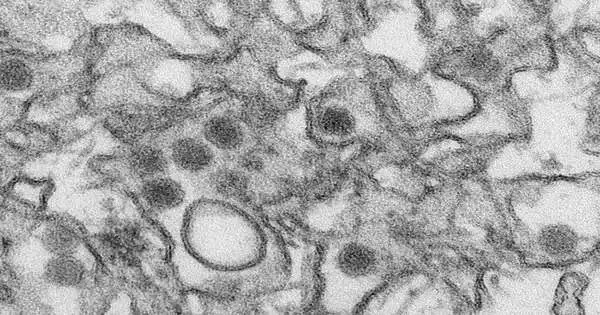
Infections have restricted hereditary material—and scarcely any proteins—so every one of the pieces should buckle down. Zika is an extraordinary model; the infection just creates 10 proteins. Presently, in a review distributed in the journal PLOS Microorganisms, scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys have shown how the infection accomplishes such a great deal with nearly nothing and may have distinguished a restorative weakness. In the review, the exploration group showed that Zika's catalyst—NS2B-NS3—is a multipurpose device with two fundamental capabilities: separating proteins (a protease) and partitioning its own twofold abandoned RNA into single strands (a helicase). "We found that Zika's compound
A protein in a safe framework customized to shield the body from contagious contaminations is likewise responsible for worsening the seriousness of specific immune system illnesses like peevish gut sickness (IBS), type 1 diabetes, dermatitis, and other persistent problems, a new examination from the Australian Public College (ANU) has found. The disclosure could make way for new and more viable medications without the awful symptoms of existing medicines. As well as assisting with overseeing serious immune system conditions, the advancement could likewise assist with treating a wide range of diseases. The work has been distributed in Science Advances. The researchers
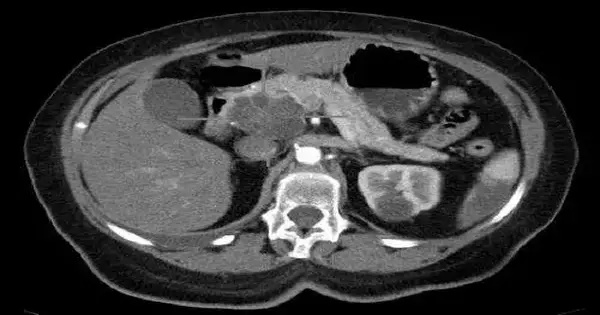
The preclinical examination distributed in the diary for immunotherapy of malignant growth focuses on a promising new therapy choice for individuals with pancreatic disease. Scientists from the VCU Massey Thorough Disease Community and the VCU Establishment of Sub-atomic Medication (VIMM) propose that when utilized in a structure that can be conveyed straightforwardly into the growth cell, polyinosine-polycytidylic corrosive (pIC) stifles cancer development, prompts disease cell passing, and improves endurance in creature models with the most widely recognized type of pancreatic malignant growth. Specialists likewise presumed that when utilized alone or in blend with a standard of care medicine, for example,
Consistently, north of 15,500 Australians are determined to have entrail malignant growth, and it is the subsequent driving reason for disease passings in the country. North of 1,700 (one out of 10) of those analyzed are youthful Australians matured under 50, and this occurrence is expanding. There is an earnest need to find more successful therapies and further develop gut disease screening, especially for the beginning stages of malignant growth (those aged 25–49 years). Australians brought into the world in 1990 onwards have twofold the gamble of creating entrail malignant growth compared to those brought into the world in 1950.
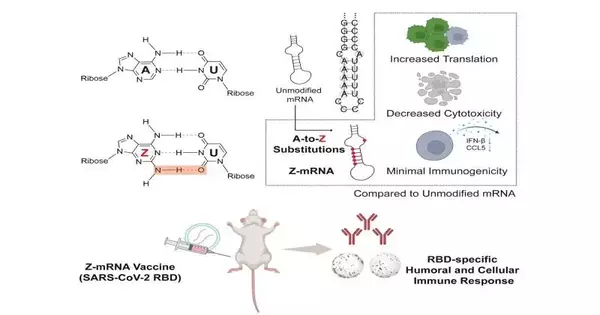
Courier RNA (mRNA) innovation has become well known over the most recent couple of years because of its utilization in coronavirus antibodies. This innovation has been momentous to such an extent that it, as of late, won the 2023 Nobel Prize in medication "for revelations concerning nucleoside base alterations that empowered the advancement of powerful mRNA immunizations against Coronavirus." This isn't a new innovation, but adjusted mRNAs have been around for a really long time and show huge potential for helpful applications. Contrasted with unmodified mRNAs, changed mRNAs are more steady and have better immunogenic impacts. A group of scientists
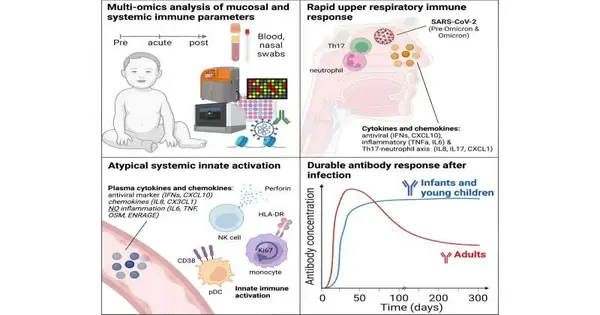
Research driven by the College of Tübingen, Germany, alongside accomplices at Stanford College, Emory College, and the Cincinnati Kids' Clinic Clinical Center, U.S., has investigated baby invulnerable reactions following SARS-CoV-2 contaminations during the underlying long periods of life. In a paper named "Multi-omics examination of mucosal and fundamental resistance to SARS-CoV-2 after birth," distributed in Cell, the exploration group finds that babies and small kids mount solid neutralizer reactions for as long as 300 days. There has been an absence of an exhaustive, framework-wide, longitudinal examination of how babies and small kids respond to SARS-CoV-2 contamination with respect to their