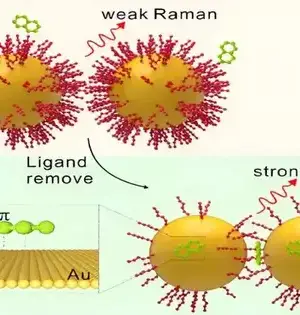
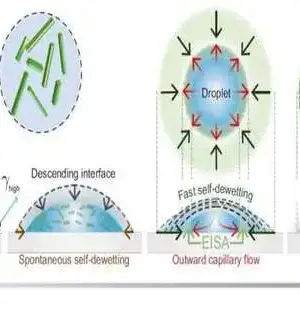
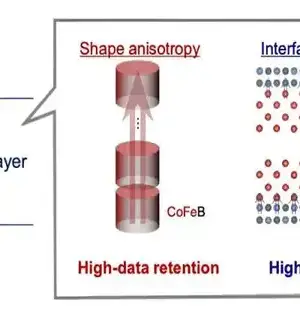
Ethanol power modules are viewed as promising wellsprings of green power. In any case, costly platinum impetuses are utilized in their creation. Research on laser softening of suspensions completed at the Establishment of Atomic Physical Science of the Clean Foundation of Sciences in Cracow has driven specialists to materials that catalyze ethanol with a comparable—and possibly considerably more noteworthy—productivity to platinum yet are made of a component that is commonly less expensive than platinum. At the point when a laser beats light on a suspension of nanoparticles, the particles in the suspension can start to liquefy and stay together for
Nanotechnology
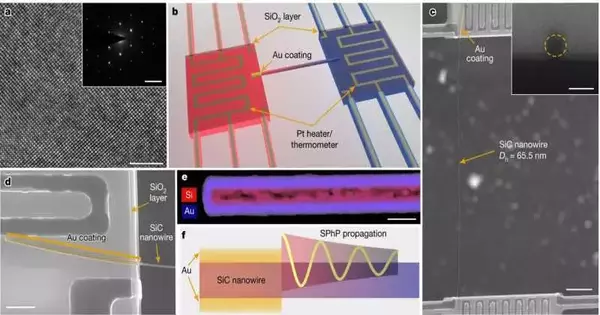
Vanderbilt mechanical design teachers Deyu Li and Josh Caldwell are important for a group of scientists who have found another intensity scattering channel involving phonon polaritons that could have broad ramifications for novel cooling advancements in gadgets like PDAs and other current hardware. The examination was, as of late, distributed in Nature under the title "Striking Intensity Conduction Interceded by Non-Harmony Phonon Polaritons." It is notable that electrons and nuclear vibrations (phonons) are the significant energy transporters in solids. Research groups from Vanderbilt College and Oak Edge Public Lab (ORNL) were astonished to find that surface phonon polaritons, half-breed semiparticles
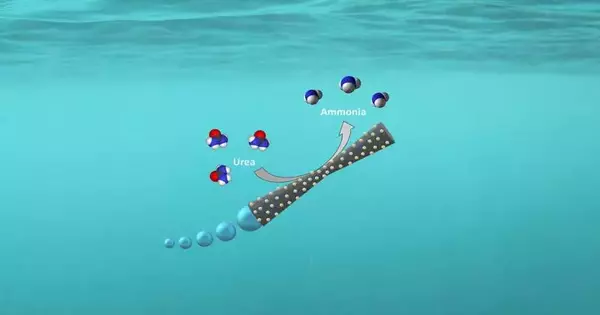
Analysts from ICIQ in Spain have planned micromotors that move around all alone to filter wastewater. The cycle makes smelling salts, which can act as an environmentally friendly power source. Presently, a man-made intelligence strategy created at the College of Gothenburg will be utilized to tune the engines to accomplish the most ideal outcomes. Micromotors have arisen as a promising device for natural remediation, to a great extent because of their capacity to independently explore and perform explicit errands on a microscale. The micromotor is contained in a cylinder made of silicon and manganese dioxide, in which synthetic responses cause
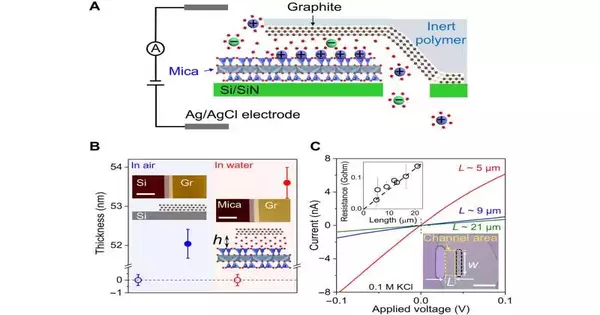
Materials researchers have widely concentrated on quick particle pervasion in nanofluidic diverts for a long time because of their true capacity inside filtration advancements and osmotic energy collection. While the components hidden particle transport still can't seem to be perceived, the cycle can be accomplished in nanochannels created in a painstakingly controlled way. In another report presently distributed in Science Advances, Yu Jiang and an exploration group in the actual science of strong surfaces in China depicted the improvement of two-layered nanochannels with their top and base walls containing molecularly level graphite and mica precious stones. The unmistakable wall designs
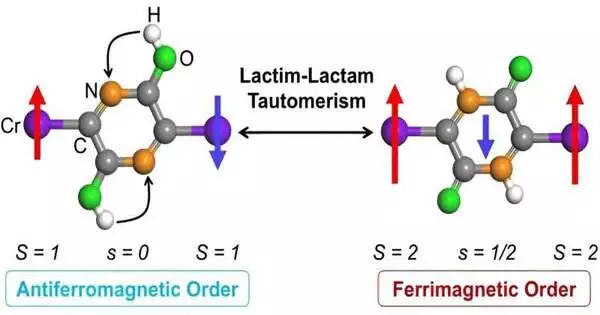
An examination group led by Partner Prof. Li Xingxing and Prof. Yang Jinlong from the College of Science and Innovation of China (USTC) of the Chinese Foundation of Sciences (CAS) has fostered a pivotal substance strategy for two-layered metal-natural cross sections. Their outcomes were distributed in Nano Letters on October 2. In spintronics, it is vital to foster an effective approach to reversibly controlling the twist requests of materials. However, different actual techniques have been proposed, and synthetically accomplishing this has presented critical difficulties. Specialists proposed the usage of the all-around perceived lactim-lactam tautomerization cycle to reversibly regulate the attractive
The manner in which light communicates with normally occurring materials is surely known in physical science and materials science. Yet, in many years, analysts have manufactured metamaterials that cooperate with light in new ways that go past, as far as possible, forcing on normally occurring materials. A metamaterial is made out of varieties of "meta-molecules," which have been created into beneficial designs with a size of around 100 nanometers. The design of varieties of meta-iotas works with exact light-matter cooperation. In any case, the enormous size of meta-iotas compared with normal particles, which are more modest than a nanometer, has
Interestingly, researchers and designers have seen continuously how two sorts of nanoparticles produced using various materials join into new composite materials. The discoveries, detailed by a group led by the College of Pennsylvania and the College of Michigan, could assist engineers with having more command over the gathering of materials that combine the beneficial properties of every molecule—for example, photoluminescence, attraction, and the capacity to direct power. "We are planning new materials that join various types of capabilities in manners that are impractical with the materials we have today," said Sharon Glotzer, the Anthony C. Lembke Division Seat of Substance
With the fast advancement of industrialization, water contamination is turning out to be increasingly serious. The customary water treatment technique can't really eliminate natural contamination, so high-level oxidation innovation has turned into a potential arrangement. As a possible substance oxidant, permanganate (KMnO4) has been generally read up for water purification because of its high proficiency, cost-viability, and high security. Be that as it may, the unfortunate soundness and restricted oxidation potential (1.68V) of KMnO4 limit its applications. To overcome these issues, scientists have attempted different imaginative ways to deal with the reactivity of KMnO4. Sadly, on account of the expansion
Scientists from the Public Establishment of Data and Correspondences Innovation have imagined an original construction in a superconducting strip photon locator that empowers profoundly effective photon discovery even with a wide strip and prevailed with regards to fostering the world's most memorable Superconducting Wide-Strip Photon Identifier (SWSPD). The strip width of the locator is nearly 200 times more extensive than that of the traditional superconducting nanostrip photon identifiers (SNSPDs). This innovation can assist with tackling the issues of low efficiency and polarization reliance that exist in traditional SNSPDs. The new SWSPD is supposed to be applied to different cutting-edge innovations
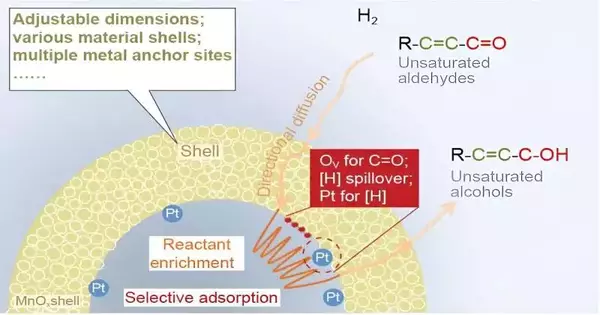
Empty, organized, upheld metal impetuses (for example, nanoreactor impetuses) with embodied dynamic destinations and obvious shells give an optimal spot to multicomponents to respond or change helpfully in a methodical way, and proficiently have been perceived as one of the most well-known impetus applicants. Despite the fact that reactant improvement has been proposed by exploring the connection between synergist execution and the construction of nanoreactors at the nanolevel, the investigation of the enhancement impact at the mesoscale (500–2000 nm) is not yet thorough enough. Building the nanoreactor models with dynamic metals inside and outside the empty nanostructure by means of