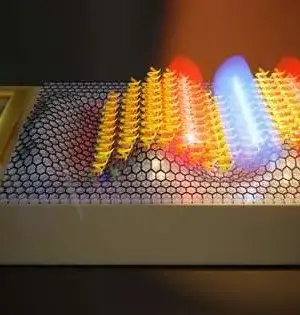
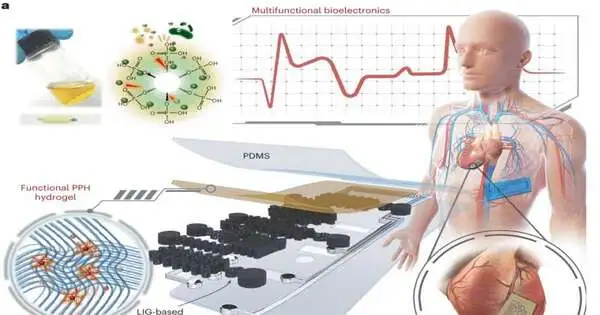
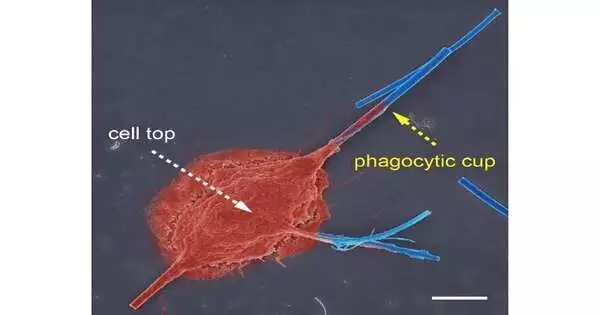
A new report distributed in Nature Hardware examines stretchable graphene-hydrogel interfaces for wearable and implantable bioelectronics. Stretchable and conductive nanocomposites with precisely delicate, meager, and biocompatible highlights assume imperative roles in creating wearable skin-like gadgets, savvy, delicate robots, and implantable bioelectronics. Albeit a few plan procedures, including surface design, have been accounted for to beat the mechanical jumble between the weak cathodes and stretchable polymers, it is yet to be tested to acknowledge a solid combination of different parts with different functionalities utilizing the current ultrathin stretchable conductive nanocomposites. This is credited to the absence of reasonable conductive nanomaterial frameworks
Bio & Medicine
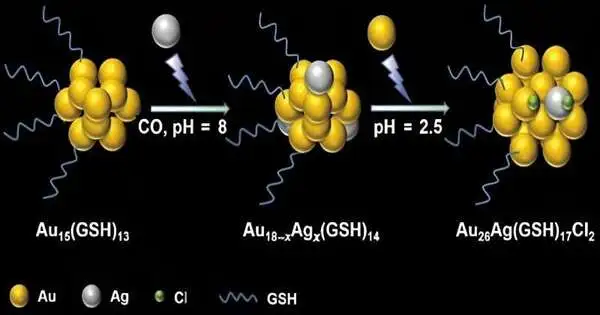
Lately, ultrasmall metal nanoclusters have made progress in fields ranging from bioimaging and biosensing to biotherapy, on account of their exceptional atomic-like properties. In a review distributed in the diary Polyoxometalates, an examination group from Qingdao College of Science and Innovation proposed a plan to orchestrate molecularly exact, water-dissolvable compound nanoclusters. "The oddity of this study is another methodology for the blend of water-solvent compound nanoclusters and a further commitment to the major comprehension of the alloying system of metal nanoclusters," said concentrate creator Xun Yuan from Qingdao College of Science and Innovation. "A definitive objective is to foster such
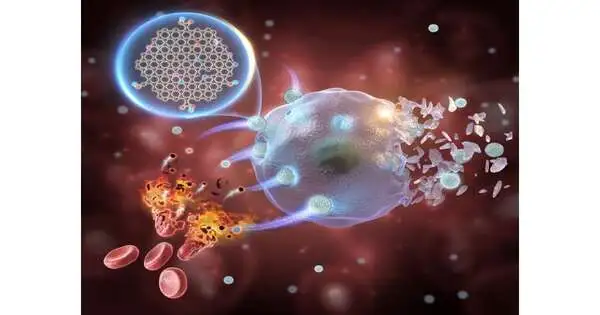
An exploration group led by Prof. Wang Hui from the Hefei Foundations of Actual Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Institute of Sciences has presented a non-metal nanozyme in view of graphene quantum specks (GQDs) for exceptionally productive growth chemodynamic treatment (CDT). The review is distributed in Issue. GQDs address a promising and savvy method for tending to the harmful concerns related to metal-based nanozymes in cancer CDT. In any case, the restricted synergist movement of GQDs has presented critical difficulties for their clinical application, especially under testing reactant conditions. "The GQDs, which are produced using red platelet films, are exceptionally
The pathogenic capability of breathing in the latent sinewy nanomaterials utilized in warm protection (like asbestos or fiberglass) is really associated not with their substance synthesis but rather with their mathematical attributes and size. The justification behind this is the failure of the macrophages normally present in pneumonic alveolar tissue to dispose of unfamiliar bodies that are excessively huge. This finding was uncovered in a concentrate on glass nanofibers by a French-Chinese group, including a CNRS scientific expert. The examination was distributed on January 3, 2024, in the journal Nature Nanotechnology. The review was initially directed in vitro at electrochemical
Utilizing another innovation created at MIT, diagnosing cellular breakdown in the lungs could become as simple as breathing in nanoparticle sensors and, afterward, taking a pee test that uncovers whether a growth is available. The new symptom depends on nanosensors that can be conveyed by an inhaler or a nebulizer. Assuming the sensors experience malignant growth-connected proteins in the lungs, they produce a sign that gathers in the pee, where it very well may be recognized with a straightforward paper test strip. This approach might actually supplant or enhance the ongoing best quality level for diagnosing cellular breakdown in the
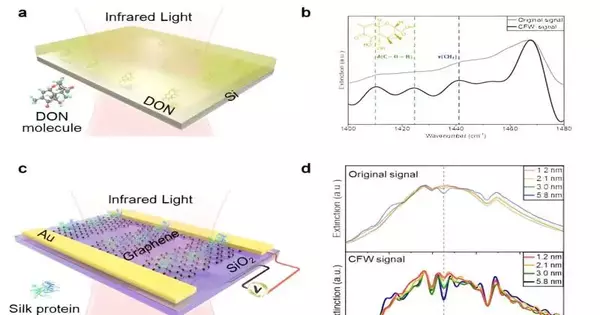
Sensors are fundamental devices for identifying and breaking down particles in different fields, including natural observation, food handling, and general wellbeing. In any case, creating sensors with a sufficiently high aversion to recognizing these little particles remains a test. One promising methodology is surface-improved infrared ingestion (SEIRA), which utilizes plasmonic nanostructures to enhance the infrared signs of atoms adsorbed on their surface. Graphene is an especially encouraging material for SEIRA in light of its high responsiveness and tunability. Nonetheless, the association between graphene and atoms is debilitated by inborn sub-atomic damping. In another paper distributed in eLight, specialists from numerous
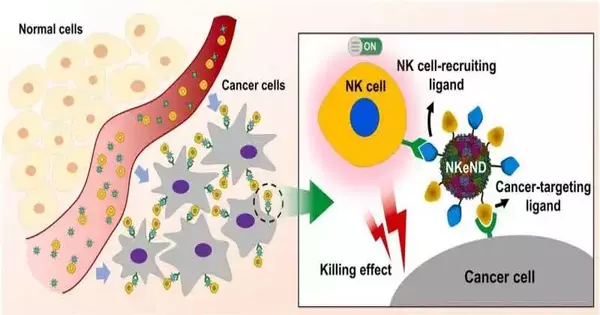
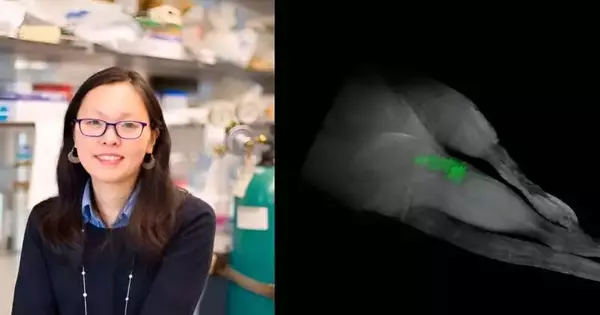
A review conducted by Teacher Sebyung Kang and Teacher Sung Ho Park in the Division of Natural Sciences at UNIST has uncovered an exceptional forward leap in disease treatment. The examination group has effectively evolved extraordinary "NK cell-connecting with nanodrones," able to specifically focus on and take out disease cells, offering an expected answer for immovable kinds of tumors. The inborn lymphoid cells, known as regular executioner (NK) cells, assume an essential role in the body's resistance to disease. Various endeavors have been made to harness the force of NK cells to foster powerful malignant growth treatments. Presently, the examination
The layer that encases an organic cell isn't just a hindrance; it is packed with proteins associated with a wide range of basic natural capabilities. To truly comprehend what layer proteins are doing and how, analysts need to realize how they're coordinated and the way that they communicate with each other. However, it is trying to uncover that data. Yale scientists have now fostered another microscopy technique called Local nanoBleach that defeats the primary difficulties to figuring out film protein association, remembering the trouble of concentrating on these layers without upsetting the local climate and cutoff points to the goal
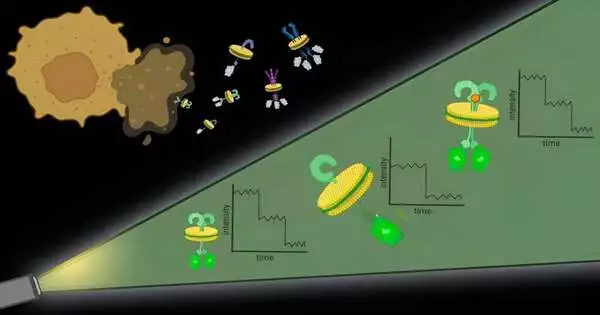
With regards to conveying medications to the body, a significant test is guaranteeing that they stay in the space they're treating and proceeding to precisely convey their payload. While significant steps have been made in conveying drugs, checking them is a test that frequently requires obtrusive methodologies like biopsies. Analysts at NYU Tandon, led by Jin Kim Montclare, Teacher of Substance and Biomolecular Designing, have created proteins that can collect themselves into filaments to be utilized as restorative specialists for possible medicines for different sicknesses. These biomaterials can embody and convey therapeutics for a large group of illnesses. Yet, while
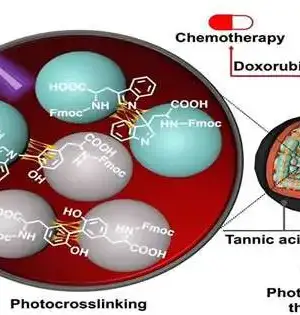
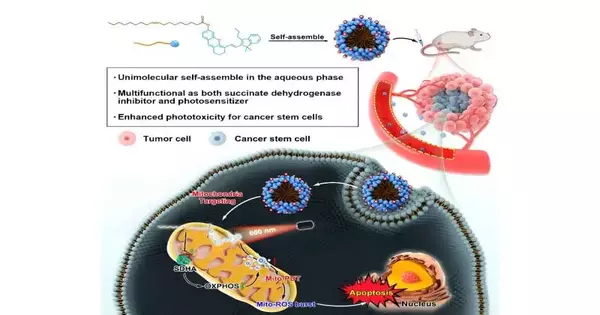
Malignant growth foundational microorganisms (CSCs) are an uncommon population of cells in cancer tissues that drive tumorigenesis, repeat, and metastasis. Subsequently, the improvement of hostile growth treatments that can take out CSCs has huge ramifications for disease treatment. Photodynamic treatment (PDT) is a remedial methodology that utilizes a particular laser frequency to initiate photosensitizers, producing a lot of receptive oxygen species (ROS) to repress cancer development specifically. In any case, taking into account that oxygen is essential for type II PDT and that hypoxia breeds CSCs, PDT is ineffectual for those CSCs that are established in hypoxic cancer regions. Accessible