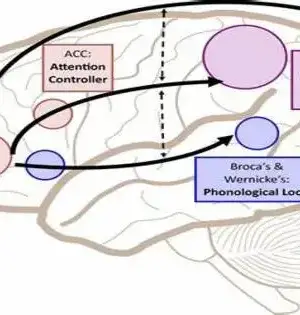
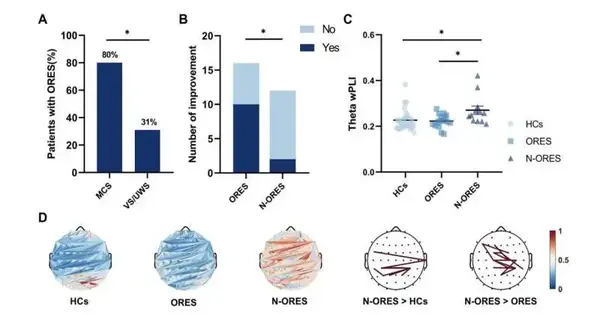
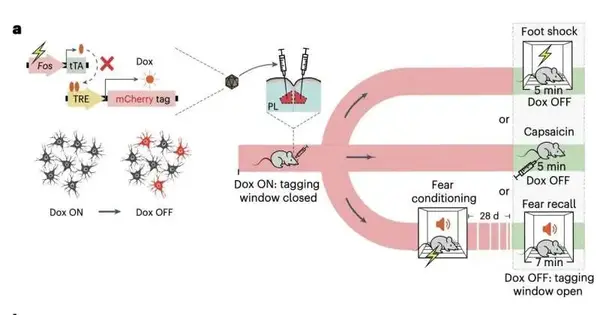
Serious cerebrum wounds or head injuries in people can prompt different phases of purported problems of cognizance (DoC). Consciousness is either partially or completely absent in these states, such as a coma, a condition known as unresponsive wakefulness syndrome or a vegetative state, and a state of minimal awareness. Because it enables medical professionals to determine which treatments to administer and how to facilitate the re-emergence of consciousness, accurately evaluating patients who have lost consciousness is of the utmost significance. When conducting a clinical evaluation of consciousness, doctors typically observe how patients respond to sensory stimuli like sounds or images.
Neuroscience
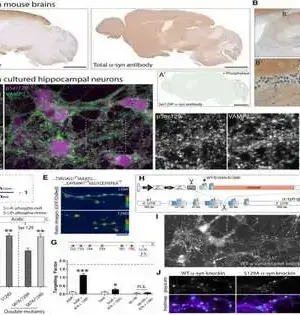
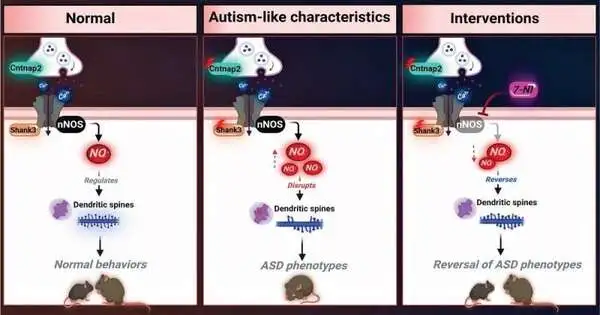
Nitric oxide production in the brain is linked to autistic symptoms, according to Israeli researchers at the University of Haifa and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. The researchers describe how an initial observation in a mouse study led to a deeper investigation into the activity of nitric oxide and the discovery of a quantity-dependent causative correlation to disease pathology in their paper, "The NO Answer for Autism Spectrum Disorder," which was published in Advanced Science. The review results show that nitric oxide (NO) plays a part in mental imbalance range jumble (ASD) improvement and influences synaptogenesis and the glutamatergic and
New UCL research has revealed the biology of a rare genetic mutation that enables its carrier to live virtually pain-free, heal more quickly, and experience less anxiety and fear. The team's discovery of the FAAH-OUT gene and the rare mutations that cause Jo Cameron to experience virtually no pain and never feel anxious or afraid in 2019 is the basis for the study, which was published in Brain. The new study explains how the FAAH-OUT mutation "turns down" FAAH gene expression and how it has knock-on effects on other molecular pathways related to mood and wound healing. New drug targets
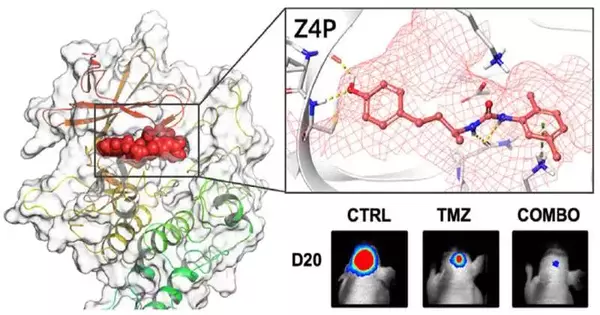
In collaboration with colleagues in France, researchers at the University of Gothenburg have developed a method that successfully kills the aggressive brain tumor glioblastoma. The cancer dies from stress as a result of a docked molecule blocking certain cell functions. Disease cells, particularly those that structure forceful growths, are somehow wild and carry on with an exceptionally distressing reality. Cancer cells hijack mechanisms that healthy cells use to regulate protein production and process the excess proteins they produce in order to manage this stress. The cancer cell would die if these hijacked mechanisms continued. "We have now prevailed with regards
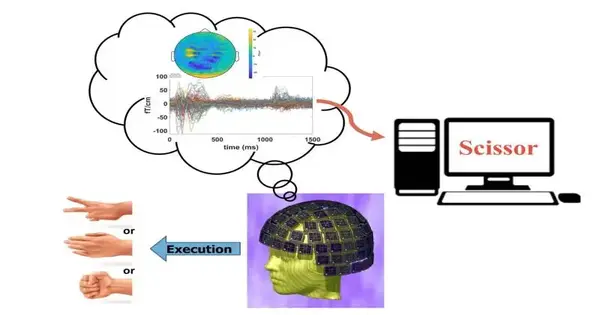
By only looking at data from noninvasive brain imaging without taking into account information from the hands themselves, researchers at the University of California, San Diego, were able to distinguish between different hand gestures that people were using. The outcomes are an early move toward fostering a harmless cerebrum PC interface that may one day permit patients with loss of motion, cut-off appendages, or other actual difficulties to utilize their psyche to control a gadget that helps with regular undertakings. The study, which was recently published online ahead of print in the journal Cerebral Cortex, is the best one yet
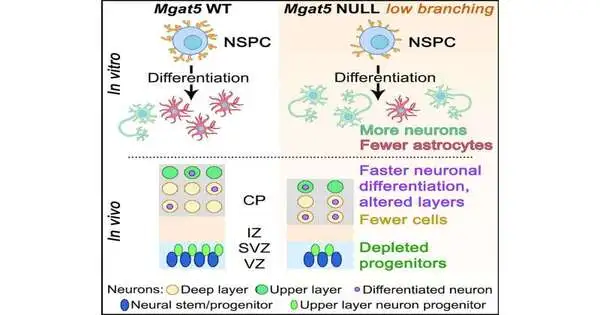
A study by researchers at the University of California, Irvine, found that the MGAT5 glycosylation enzyme is important for brain development. This could lead to new uses for neural stem cells in medicine. The final mature cells of the brain and spinal cord that are produced by neural stem cells are oligodendrocytes, neurons, and astrocytes. Each has particular and key capabilities. Signals are sent by neurons, modified by astrocytes, and preserved by oligodendrocytes in the brain. Small sugar molecules are frequently added by cells when they make proteins or fats that end up on the cell surface. The team investigated
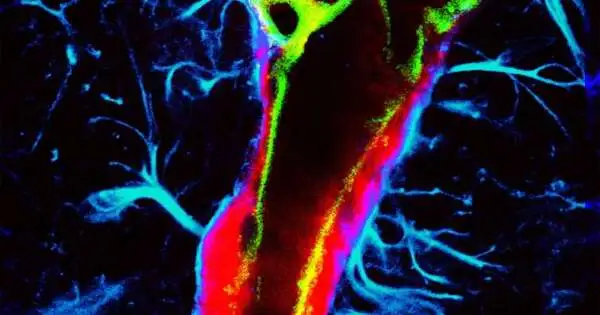
The glymphatic system in the brain, like the lymphatic system in the body, distributes nutrients and other essential compounds and eliminates metabolic waste. Weaknesses in this framework might add to mental illnesses like neurodegenerative illnesses and stroke. The McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis has developed a focused ultrasound-based, non-pharmaceutical method for influencing glymphatic transport, paving the way for further research into brain diseases and brain function. The consequences of the work are distributed in the Procedures of the Public Foundation of Sciences on May 15. The first direct evidence that focused ultrasound, combined with circulating
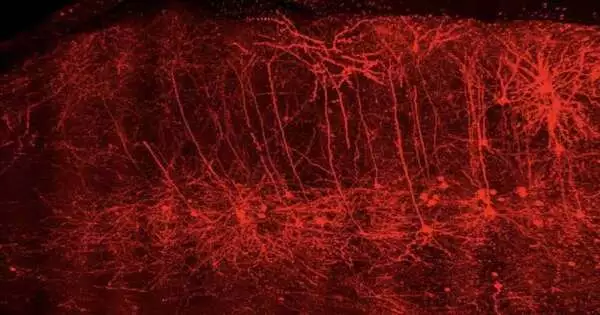
A group of neuroscientists at the Clinical College of South Carolina (MUSC) has recognized changes in the movement of synapses known as pyramidal neurons, which add to what medicate is looking for in a preclinical model of narcotic use issues. These neurons became more excited when heroin access was restricted. The movement of these neurons was reestablished to typical levels by impeding the chemical protein kinase A (PKA). Restraining this catalyst additionally decreased narcotic looking for conduct. The findings of their team were recently published in the Journal of Neuroscience by Jacqueline McGinty, Ph.D., a professor of neuroscience, and Saurabh
While agony and dread are altogether different encounters, past investigations have demonstrated the way that they can, in some cases, be firmly connected with each other. For instance, when a lot of animals and people are in dangerous or life-threatening situations, acute fear can prevent them from feeling pain and allow them to fully concentrate on what is going on. On the other hand, research showed that when people experience elevated degrees of agony, they can make long-term and cooperative trepidation recollections that make them unfortunate of the circumstances that they associate with the aggravation they felt. These memories can,
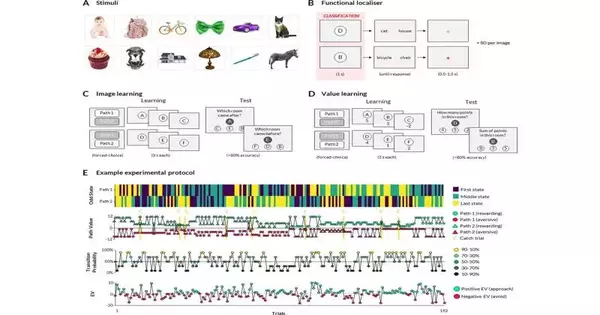
Past neuroscience studies propose that while concluding their next activities, mice and different rodents will generally replay previous results of comparative circumstances in their minds, which is reflected in a quick enactment of specific cerebrum districts in succession. As of late, a few examinations have kept comparative replay-related cerebrum action in the human mind by utilizing imaging strategies. A study by UCL researchers looked into the possibility that this rapid "replay" of positive and negative outcomes from the past could predict how people will act in a situation where they could lose or gain money. Their findings, which were published